Boundary Layer in a Concave Bend
Experiments by Johnson
Description
Developing boundary layer submitted to destabilizing concave curvature at Reθ=1450Reθ=1450 without longitudinal pressure gradient (S=∂p/∂x≈0S=∂p/∂x≈0).
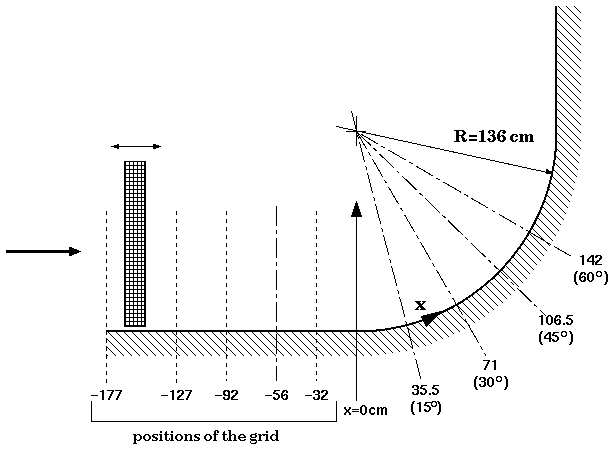
The test facility is a free surface water channel, shown schematically in figure 1, consisting of an asymmetric 4:1 contraction, a 4.88 m long straight development section with dimensions 25 cm (width) by 1.25m (span), a 90 degree constant radius curved wall (R=−136R=−136 cm), and a straight recovery section. The channel walls are contoured to minimize pressure gradient in the straight development section and along the concave test surface. The boundary layer is tripped 1 m downstream of the nozzle exit using a 0.476 cm square rod. Spanwise surveys show good spanwise uniformity; specifically, the roll cells which appear in the curved section are not fixed in space, but are randomly distributed in space and time.
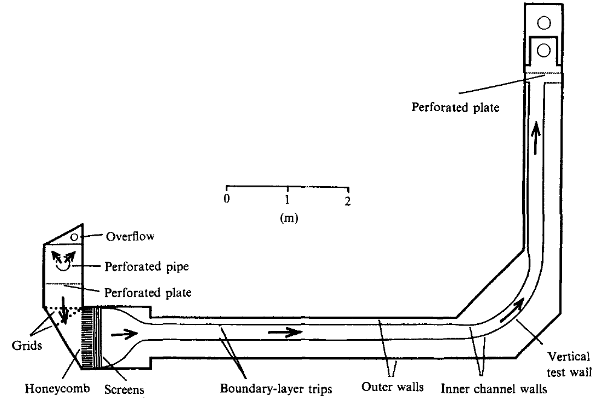 Fig. 1: Experimental arrangement
Fig. 1: Experimental arrangement
LDV measurements of all three velocity-component were made down to y+≈5y+≈5; u′ and w′ are at even smaller y+ at a number of streamwise locations, as indicated in figure 2.
One set of measurements were taken with no grid-generated turbulence present (without the grid shown in figure 2). For the other sets, a square, biplanar, square bar grid (mesh spacing M=6.35 cm; ratio of mesh spacing to bar width M/w=4) was placed at various locations upstream of the curved wall and used to generate nearly axisymmetric turbulence. In most cases the free-stream turbulence levels were nominally u′/Upw=0.05.
Measurement Techniques
Velocities measured using LDV.
Available Measurements
For most cases profiles are available at a number of streamwise locations around the bend for
- Mean velocity
- Reynolds stresses
- Triple moments, skewness, flatness
Sample plots of selected quantities are available.
The data can be downloaded as compressed archives from the links below, or as individual files.
The file readme.txt contains a description of the files and data formats.
xdata.dat contains a summary of the channel width as a function of streamwise distance, and values of wall skin friction at measurement locations.
| Cases Without Turbulence-Generating Grid | ||
|---|---|---|
| Location | Mean velocity & Reynolds stresses | Triple moments |
| x=−56 cm | fn1.dat | fn2.dat |
| x=35.5 cm (15o station) | cn151.dat | cn152.dat |
| x=71 cm (30o station) | cn301.dat | cn302.dat |
| x=106.5 cm (45o station) | cn451.dat | cn452.dat |
| x=142 cm (60o station) | cn601.dat | cn602.dat |
| Cases With Turbulence-Generating Grids | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Mean velocity & Reynolds stresses | Triple moments | Notes |
| x=−56 cm | fg191.dat | Grid placed at x=−177 cm | |
| x=−56 cm | fg101.dat | Grid placed at x=−120 cm | |
| x=35.5 cm (15o station) | cg151.dat | cg152.dat | Grid placed at x=−127 cm |
| x=71 cm (30o station) | cg301.dat | cg302.dat | Grid placed at x=−92 cm |
| x=106.5 cm (45o station) | cg451.dat | cg452.dat | Grid placed at x=−56 cm |
| x=142 cm (60o station) | cg601.dat | cg602.dat | Grid placed at x=−32 cm |
References
- Barlow, R.S., Johnston, J.P. (1988). Structure of a turbulent boundary layer on a concave surface. J. Fluid Mech., Vol. 191, pp. 137-176.
- Johnson, P.L. (1990). PhD thesis, Stanford University.
- Johnson, P.L., Johnston, J.P. (1989). The effects of grid-generated turbulence on a flat and concave turbulent boundary layer. Report MD-53, Thermosciences Division, Dept. of Mech. Eng., Stanford University.
Indexed data:
| case023 (dbcase, confined_flow) | |
|---|---|
| case | 023 |
| title | Boundary Layer in a Concave Bend |
| author | Johnson |
| year | 1990 |
| type | EXP |
| flow_tag | 2d, curvature |