Table of Contents
Natural Convective Vertical Boundary Layer
Experiments by Tsuji and Nagano
Description
Turbulent natural convective boundary layer along a vertical heated copper plate. 2D incompressible air flow with temperature and density variation.
Experimental Arrangement
The experimental arrangement is shown in figure 1. The boundary layer develops over the 1m wide by 4m long flat plate, which is heated via a series of steel strip heaters, controlled in such a way to produce a constant plate surface temperature.
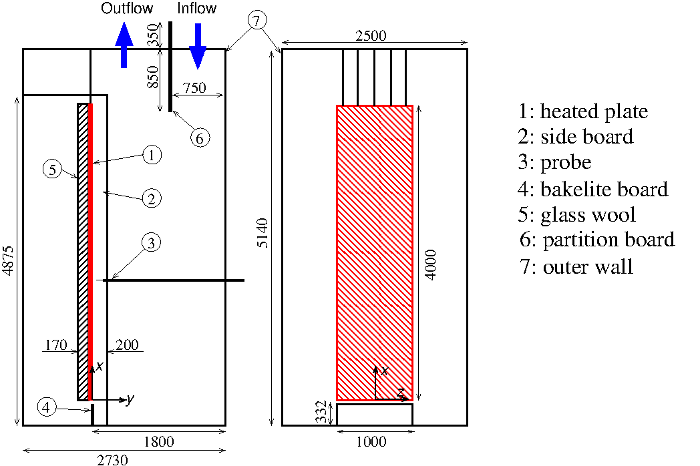 Fig. 1: Experimental arrangement
Fig. 1: Experimental arrangement
Velocity and temperature measurements are provided at four locations along the plate: 1.44 m, 1.92 m, 2.54 m and 3.24 m from the leading edge.
Flow Characteristics
Turbulence in this kind of flow is driven by buoyancy forces in such a way that relatively large fluctuations of velocity and temperature take place at low velocity.
The copper plate generating the flow is 4 m long and 1 m wide. It is suspended in a sufficiently large room. The leading edge of the plate is chamfered in order to allow a stable laminar boundary layer to develop. Two-dimensionality is ensured by side boards on both sides of the plate. The surface is heated to a constant temperature, and the boundary layer becomes naturally turbulent at about \(x = 0.8\) m above the leading edge.
Flow Parameters
- Ambient temperature: \(T_a = 16\)oC.
- Ambient kinematic viscosity: \(\nu = 1.67 \times 10^{-5}\) m2/s.
- Ambient atmospheric pressure: \(p_a = 1017\) hPa.
- Heated surface temperature: \(T_w = 60\)oC (some heat transfer measurements also available with \(T_w = 100\)oC).
- Prandtl number: \(Pr = 0.71\).
- Grashof number: \(Gr_x = g(T_w - T_a)x^3/((273. + T_a)\nu^2) = 5.50 \times 10^9 x^3\).
- Nusselt number: \(Nu_x = q_wx/((T_w - T_a)\lambda_w)\), where \(q_w\) is the wall heat flux and \(\lambda_w\) is the thermal conductivity.
- Reference velocity: \(U_b = (g(T_w - T_a)\nu/(273. + T_a))^{1/3} = 0.0295\) m/s.
Inflow Conditions
Simulations of the flow could be started from the leading edge of the plate, with uniform ambient conditions, in order to capture the entire boundary layer development, including transition.
For those wishing to start calculations further downstream, the measurements at \(x=1.44\) m could be used to represent the partially developed turbulent boundary layer there. Data at this location (stored in files nw_bl004.dat and nw_bl007.dat) include:
- Velocity measurements. Profiles of:
- First order moment: \(U^+ = U/u_{\tau}\)
- Second order moments: \(u'/u_{\tau}\), \(\overline{uv}/(u_{\tau})^2\).
- Temperature measurements. Profiles of:
- First order moment: \(\Theta^+ = (T_w - \Theta)/t_{\tau}\).
- Second order moments: \((\overline{\theta^2})^{1/2}/t_{\tau}\), \(\overline{u\theta}/(t_{\tau} u_{\tau})\), \(\overline{v\theta}/(t_{\tau} u_{\tau})\)
Experimental Details
Fluid temperature and velocity have been measured using a normal hot wire coupled to a cold wire. Several measurements have been carried out at nearly the same locations but with different Grashof numbers.
Fluid temperature close to the wall has been measured using a platinum-rhodium-platinum thermocouple up to \(y^+ = 4\).
Ambient temperature \(T_a\) has been measured using seven thermocouples placed 600 mm away from the heated surface.
Surface temperature \(T_w\) has been measured using copper-constantan thermocouples embedded in the back of the vertical plate.
The friction velocity is defined as: \(u_{\tau} = (\tau_w/\rho)^{1/2}\) where \(\tau_w\) is the wall shear stress.
The wall shear stress is obtained from \(\partial U/\partial y|_{y=0}\).
The friction temperature is defined as: \(t_{\tau} = q_w/\rho C_pU^*\) where \(C_p\) is the specific heat at constant pressure.
The wall heat flux is defined as: \(q_w = -\lambda_w(\partial\Theta/\partial y)_{y=0}\) and determined from the measured temperature gradient at the wall.
Measurement Errors:
| \(\delta(y)\) | \(\pm 0.13\) | \(\delta(\Theta/t_{\tau})\) | \(\pm 0.14\) |
| \(\delta(U/u_{\tau})\) | \(\pm 0.14\) | \(\delta(W/u_{\tau})\) | \(\pm 0.24\) |
| \(\delta(u'/u_{\tau})\) | \(\pm 0.04\) | \(\delta(w'/u_{\tau})\) | \(\pm 0.03\) |
| \(\delta(\overline{uw}/(u_{\tau})^2)\) | \(\pm 0.08\) | \(\delta((\overline{\theta^2})^{1/2}/t_{\tau})\) | \(\pm 0.05\) |
| \(\delta(\overline{u\theta}/(t_{\tau}u_{\tau}))\) | \(\pm 0.07\) | \(\delta(\overline{w\theta}/(t_{\tau}u_{\tau}))\) | \(\pm 0.05\) |
Available Measurements
The data is stored in five files, which can be downloaded as compressed archives from the links below, or as individual files.
Sample plots of selected quantities are available.
Nusselt Number and Wall Shear Stress
Part of the data in file nw_bl004.dat represents:
- Evolution of the local Nusselt number (\(Nu_x\)) along the plate, between approximately \(0.113 < x < 3.703\) m
- Evolution of the wall shear stress (\(\tau_w/(\rho U_b^2)\)) along the plate, between approximately \(0.307 < x < 3.244\) m
Profiles Across the Boundary Layer
Stored in files nw_bl004.dat and nw_bl007.dat are profiles across the boundary layer, at four locations (\(x=1.438\), \(1.918\), \(2.535\) and \(3.264\) m, corresponding to \(Gr_x=1.55\times 10^{10}\), \(3.62\times 10^{10}\), \(8.44\times 10^{10}\) and \(1.80\times 10^{11}\)) of:
- Velocity measurements.
- First order moment: \(U^+ = U/u_{\tau}\)
- Second order moments: \(u'/u_{\tau}\), \(\overline{uv}/u_{\tau}^2\)
- Temperature measurements.
- First order moment \(\Theta^+ = (T_w - \Theta)/t_{\tau}\)
- Second order moments: \((\overline{\theta^2})^{1/2}/t_{\tau}\), \(\overline{u\theta}/(t_{\tau}u_{\tau})\), \(\overline{v\theta}/(t_{\tau}u_{\tau})\)
Stored in file nw_bl006.dat are profiles at \(x = 2.538\) m (\(Gr_x = 7.99\times 10^10\) and \(T_w - T_a = 41.4\)oC) of:
- Velocity measurements
- First order moments: \(U^+ = U/u_{\tau}\), \(W^+ = W/u_{\tau}\)
- Second order moments: \(u'/u_{\tau}\), \(w'/u_{\tau}\), \(\overline{uw}/u_{\tau}^2\)
- Temperature measurements
- First order moment \(\Theta^+ = (T_w - \Theta)/t_{\tau}\)
- Second order moments: \((\overline{\theta^2})^{1/2}/t_{\tau}\), \(\overline{u\theta}/(t_{\tau}u_{\tau})\), \(\overline{w\theta}/(t_{\tau}u_{\tau})\)
Stored in file nw_bl005.dat are profiles at \(x=2.536\) m (\(Gr_x = 8.99\times 10^10\) and \(T_w - T_a = 45.3\)oC) of:
- Velocity measurements
- First order moments: \(U^+ = U/u_{\tau}\), \(V^+ = V/u_{\tau}\)
- Second order moments: \(u'/u_{\tau}\), \(v'/u_{\tau}\), \(\overline{uv}/u_{\tau}^2\)
- Momentum eddy diffusivity: \(\nu_t = -\overline{uv}/(\partial U/\partial y)\)
- Temperature measurements
- First order moment \(\Theta^+ = (T_w - \Theta)/t_{\tau}\)
- Second order moments: \((\overline{\theta^2})^{1/2}/t_{\tau}\), \(\overline{u\theta}/(t_{\tau}u_{\tau})\), \(\overline{v\theta}/(t_{\tau}u_{\tau})\)
- Heat eddy diffusivity: \( \alpha_t = -\overline{v\theta}/(\partial \Theta/\partial y)\)
- Turbulent Prandtl number: \(Pr_t = \nu_t/\alpha_t\)
Stored in file nw_bl008.dat are profiles at \(x=2.536\) m (\(Gr_x = 8.99\times 10^10\) and \(T_w - T_a = 45.3\)oC) of:
- Normalized budgets of \(U^2/2\), \(\overline{u^2}/2\), \(\overline{v^2}/2\), \(\overline{uv}\), \(\overline{\theta^2}/2\), \(\overline{u\theta}\) and \(\overline{v\theta}\)
- Timescales \(\tau_u = k/\varepsilon\), \(\tau_t=\overline{\theta^2}/(2\varepsilon_{\theta})\)
Recommendations for Calculations
The following suggestions were given to contributors to a collaborative workshop in which the case was studied.
Type of Calculation: Two different types of calculation can be chosen, considering either the parabolic or the elliptic problem.
Inlet Conditions: The calculation of the boundary layer could be started at \(x = 1.44\) m using the experimental values provided as inlet conditions. These values correspond to a partially developed turbulent natural convective boundary layer. Alternatively the flow development over the whole plate length could be modelled, including the transition of the boundary layer.
Heated Wall: Surface heated at a constant uniform temperature: \(T_w\).
Entrainment Boundary: For elliptic calculations, the entrainment boundary should be placed rather far away from the heated wall, typically \(y ge 500\) mm. According to the measurements there is a slight inflow in the \(-y\) direction. One should then prescribe inflow conditions as \(U=0\), \(V < 0 \), \(p=p_a\), \(\Theta =T_a\) and low values for the turbulent quantities. \(U\) and \(p\) are known, \(V\) may be computed by solving the \(y\)-momentum equation at the boundary.
Outlet Conditions: Zero gradients in \(x\) direction for the flow variables may be prescribed. If necessary, this boundary might be moved farther away in the \(x\) direction .
Previous Numerical Studies
Kato et al. (1993) used an elliptic method to calculate the turbulent boundary layer for \(T_w - T_a = 43\)oC and \(404\)oC using three different \(k\)-\(\varepsilon\) turbulence models. They all include correction terms for treating the near-wall low-Re flow. The first one uses ensemble averages and variable density. The second one uses Favre averages and variable density also. The last one uses ensemble averages and Boussinesq's approximation for incompressible flows. The authors have compared their profiles of velocities, temperature and velocity-temperature correlations with the experimental ones at \(x = 1.90\) m (\(Gr_x = 4.5\times 10^10\) and \(T_w - T_a = 43\)oC). The authors state that “the correspondence between the experiments and the present three numerical models is fairly good”. However, the first model gives slightly better results. To summarize, they fail only in predicting the \(\overline{\theta^2}\) profiles, they slightly underpredict \(\overline{u^2}\) and overpredict \(\overline{v^2}\) profiles and fully succeed in predicting \(U\), \(T\), \(\overline{uv}\) and \(\overline{v\theta}\) profiles.
Main References
Description of experiments
- Tsuji, T., Nagano, Y. (1988). Characteristics of a turbulent natural convection boundary layer along a vertical flat plate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, Vol. 31, pp. 1723-1734.
- Tsuji, T., Nagano, Y. (1988). Turbulence measurements in a natural convection boundary layer along a vertical flat plate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, Vol. 31, pp. 2101-2111.
- Nagano, Y., Tagawa, M., Tsuji, T. (1991). Thermally driven turbulent boundary layer. 8th Int. Symp. on Turbulent Shear Flows, Munich.
Previous numerical calculations
- Kato, S., Murakami, S., Yoshie, R. (1993). Experimental and numerical study on natural convection with strong density variation along a heated vertical plate. Proc. 9th Int. Symp on Turbulent Shear Flows, Kyoto, Japan.
- Henkes, R.A.W.M., Hoogendoorn, C.J. (1989). Comparison of turbulence models for the natural convection boundary layer along a heated vertical plate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, Vol.32, p.157.
- George, W.K., Capp S.P. (1979). A theory for natural convection turbulent boundary layers next to heated vertical surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, Vol.22, p.813.
- To, W.M., Humphrey, J.A.C. (1986). Numerical simulation of buoyant, turbulent flow-I. free convection along a heated, vertical flat plate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, Vol.29, p.573.
Indexed data:
| case009 (dbcase, semi_confined_flow) | |
|---|---|
| case | 009 |
| title | Natural Convection Boundary Layer |
| author | Tsuji, Nagano |
| year | 1987 |
| type | EXP |
| flow_tag | 2, scalar, buoyant, 2dbl |